Industrial heating is a major challenge for factories, warehouses and large workspaces.
Traditional heating methods, like convection-based systems, struggle with efficiency in these large-spaced environments due to high ceilings, poor insulation and the need for large volumes of air to be heated.
Infrared heating is different from the traditional forms. It offers a more efficient approach by delivering heat directly to objects and people rather than warming the air. When considering spaces such as industrial warehouses, infrared is an energy-efficient and cost-effective alternative.
Over the last couple of decades, infrared heating technology has evolved significantly. Rather than being harsh and intense like some near-infrared heaters can be, far-infrared heaters have been developed which offers a deeper and gentler warmth.
It’s clear that businesses can now benefit from industrial infrared systems in terms of improving energy efficiency, reducing costs and creating comfortable working conditions.
How does industrial infrared heating work?
Infrared heating works by emitting electromagnetic radiation. This is nothing to be alarmed about – radiation is simply a form of energy that travels. Of course, you can get different forms of radiation, including visible light and x-rays. Infrared is another form.
Infrared radiation works by transferring heat directly to objects and surfaces rather than relying on air circulation. Unlike convection heaters, which warm air that rises and dissipates, infrared heating delivers targeted warmth where it is needed.
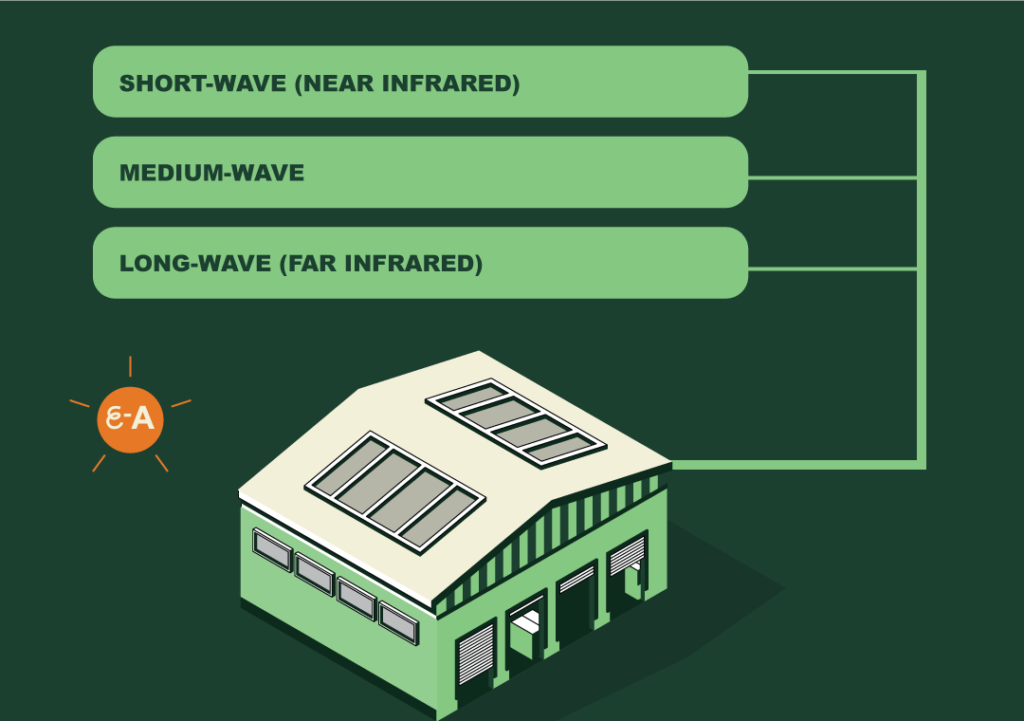
Industrial infrared systems can operate at different wavelengths. These are usually classified as:
- Short-wave (near infrared) – provides intense, almost instant heat
- Medium-wave – offers a mellow heating, good for heating materials
- Long-wave (far infrared) – provides gentle, widespread heating suitable for maintaining a good temperature in a large space. You can get far infrared industrial heaters with a large surface area which are low voltage and low temperature
By using infrared heating, businesses can achieve higher energy conversion efficiency. This is because most of the energy is directly transferred to people, equipment and surfaces instead of being lost to the surrounding air. This is particularly beneficial in industrial environments where heat retention is a challenge.
Where can an industrial infrared heating system be used?
Industrial infrared heating systems are well-suited to a wide range of places – these tend to be large, open environments with high ceilings where traditional heating methods struggle to have any sort of effect.
For this reason, you can find infrared heating in:
- Factories
- Warehouses
- Distribution centres
- Garages
- Workshops
In these industrial settings, you tend to find infrared heaters making use of their great zonal capabilities by heating primary workspaces rather than the whole facility. For example, in factories, infrared heaters can be installed above workstations or production lines to make sure employees stay warm without unnecessary energy waste.
Are there different types of industrial infrared heaters?
There are a number of different types of industrial infrared heating systems on the market. They ultimately do a similar job with the type of heat they provide, but they can be manufactured from different materials and technologies. This gives subtle differences in how they operate.
Here are some of the common infrared heaters used in industrial settings:
- Electric infrared systems – These heaters use electricity to generate infrared radiation and are highly efficient, especially in zonal heating applications. They can be mounted on walls, ceilings or work as moveable standalone heaters. Electric systems are generally much lower in carbon intensity compared to gas, especially when powered by renewable energy sources like solar panels and battery storage. These are widely used due to their excellent energy efficiencies and ability to provide near instant warmth where needed.
- Gas-fired infrared heaters – These heaters generate infrared radiation by combusting natural gas or propane. They’re often used in large industrial spaces to provide high intensity heat with potentially lower running costs. However, they require ventilation and aren’t an environmentally friendly option.
- Ceramic infrared emitters – These heaters use electricity to heat a ceramic element, which then emits infrared radiation. Ceramic heaters produce long-wave infrared heat, which is great for longer-lasting comfort.
- Quartz tube heaters – These heaters use electricity to heat a quartz element, which emits short-wave infrared radiation. They provide instant, high-intensity heat, making them suitable for spot heating in industrial settings where quick warmth is required.
- Carbon infrared systems – Using carbon-based heating elements, these heaters provide medium-wave infrared radiation.
Whilst all of these options have their advantages, electric infrared systems are often the preferred choice due to their lower environmental impact. Electricity has a lower carbon intensity than gas, making electric infrared heaters a greener option for industrial applications. Their efficiency is improved further when paired with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and battery storage. This makes electric infrared systems a future-proof and sustainable option for businesses looking to lower their environmental footprint whilst maintaining high-efficiency heating.
What are the benefits of using infrared heating in an industrial setting?

Infrared heating offers significant advantages for industrial spaces, making it a preferred choice over conventional heating systems. Unlike traditional methods that heat large volumes of air—often resulting in significant heat loss—infrared heaters provide direct, targeted warmth to people, surfaces, and objects, enhancing both efficiency and comfort.
- Energy efficiency and cost savings – Infrared heating significantly reduces energy consumption by directly warming objects rather than wasting energy heating the surrounding air. This makes it far more efficient than convection-based systems, particularly in large industrial spaces with high ceilings where heated air typically rises and dissipates. Traditional heating systems often operate at three to four times the energy input required by infrared systems to achieve the same comfort level, resulting in substantial cost savings on monthly energy expenses.
- Zonal heating – A key advantage is the ability to heat specific work zones rather than the entire facility. Infrared heaters can be strategically positioned above workstations or in high-traffic areas to help keep employees warm without wasting energy heating unoccupied areas.
- Quick heat up time – Infrared systems provide instant warmth and heat up to full power within a few minutes. This eliminates the need for long pre-heating times common with conventional systems. This rapid response allows businesses to use heating only when and where it’s needed, unlike traditional systems that must run for hours before reaching desired temperatures, leading to greater energy use and waste.
- Maintenance and installation advantages – Unlike traditional HVAC systems needing ductwork, filters and regular servicing, infrared heaters have no moving parts and require minimal maintenance. Their simple, solid-state design ensures long-term reliability and helps to reduce servicing costs and downtime. The systems offer flexible installation options, including ceiling-mounted, wall-mounted and portable options.
- Better worker comfort – Modern infrared heating systems provide consistent and comfortable warmth without creating cold drafts or uneven heat distribution when you are in the heating zone. As well as this, since these systems don’t circulate air, they prevent the movement of dust and allergens, which helps to improve air quality for employees.
- Better for the environment – Infrared heating systems help businesses reduce their carbon footprint through lower consumption of fossil fuels. When paired with renewable energy sources such as solar panels, they can operate with zero carbon emissions.
Read more on the pros and cons of infrared heating panels here.
How much do industrial infrared systems cost to run?

The cost of installing industrial infrared heating varies depending on the size of the facility you’re kitting out and the number of heaters required. To give a rough estimate, prices for a good quality industrial strength infrared heater sized at 2.5kW and above will start from £600.
For example, a Herschel Advantage IRP4 infrared heater (2.6kW) costs £999.99. This ceiling-mounted heater uses steel reflectors to project heat effectively across a 21m² area. Similarly, NexGen Rafts which are designed for workstation-specific heating cost £1,100 – £1,500 per unit.
In terms of the running costs, a 2.6kW infrared heater operating at an electricity rate of 25p per kWh would cost 65p per hour to run. If used for 8 hours per day, this equates to £5.20 per day or £156 per month per heater. Of course for an industrial setting, it’s likely that you’ll be installing more than one heater. For a large facility requiring 10 heaters, the monthly cost would be around £1,560.
The use of smart controls and zonal heating can dramatically reduce energy consumption. In one case study, a factory installed 23 x Herschel Power 4 (3.2kW) heaters, delivering a total of 73.6kW across 8 defined working zones. A conventional convector heating system would require at least 275kW to heat the entire hall, meaning the infrared system operates at just 26.8% of the comparable convector wattage, leading to significant energy and cost savings.
So, how many infrared heaters do you need?

As a general rule of thumb, 1kW of infrared heating power covers approximately 5m². This means that for a 100m² workspace, around 20kW of infrared heaters would be needed.
However, each space requires its own assessment to determine the most effective heating layout. And remember, with infrared heaters it’s all about the people and how the space is used.
As Rebecca Boehme from NexGen Heating says, “System sizes are worked out on heating people rather than whole spaces – so where there are workspaces or people working you would position an [infrared] raft.”
It’s a similar case on the domestic front when installing IR panels at home. You can read more on how many infrared panels do you need.
Tips when choosing the right system
Selecting the best industrial infrared heating system requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Heating requirements – Assessing the size of the area, work zones and temperature needs helps determine the number and type of infrared heaters required.
- Space and installation considerations – The layout of the facility will dictate whether ceiling-mounted, wall-mounted or suspended infrared heaters provide the best coverage.
- Power source availability – Choosing between electric and gas-powered infrared heaters depends on existing energy infrastructure and operational costs.
- Budget considerations – Whilst initial investment costs may be higher, the long-term savings from infrared heating justify the expense.
- Industry-specific needs – Some industries, such as food processing or paint curing, require precise heat application, making infrared technology an ideal choice.
All in all, infrared heating systems are an excellent choice for industrial settings. By focusing heat exactly where it’s needed, businesses can reduce energy waste, improve working conditions and lower costs along the way.

